

A mmol/L to mg/dL calculator is a tool used to convert measurements of blood glucose levels from millimoles per liter (mmol/L) to milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). These units are used in different parts of the world for measuring blood glucose, and the calculator helps in translating these values into the preferred local units. Use the calculator in the paragraph below:
To convert blood glucose from mmol/L to mg/dL, you typically multiply the mmol/L value by a factor, which is often around 18. This factor is based on the molecular weight of glucose and the difference in the units of measurement.
The exact calculation for Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator is:
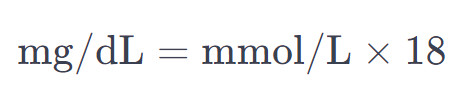
This conversion is particularly useful for people with diabetes who need to monitor their blood sugar levels and may be dealing with different measurement systems.
The Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator is a handy tool designed to convert blood glucose levels from millimoles per liter (mmol/L) to milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). This conversion is essential for individuals who are accustomed to different units of measurement and need to interpret their glucose levels accurately.
Learn more about this Calculator
To convert Mmol/L to mg/dl, you can use the following formula:
mg/dl = mmol/L × 18.01559
The formula to convert mmol/L (millimoles per liter) to mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) in the context of blood glucose measurement involves multiplying the mmol/L value by a factor, typically around 18.01559.
This factor is derived from the molecular weight of glucose. One mole of glucose weighs approximately 180.1559 grams. Since blood glucose measurements are typically in millimoles or milligrams, the weight is adjusted accordingly to maintain the units’ consistency.
When converting mmol/L to mg/dL, the formula essentially converts the concentration from a molar basis to a weight basis. This conversion is crucial in medical fields, particularly for diabetes management, as different countries use different units to measure blood glucose levels.
The precision of the conversion factor, 18.01559, provides a more accurate conversion, ensuring that medical professionals and patients can accurately interpret and compare blood glucose readings irrespective of the unit system being used.
This accuracy is vital for the effective management of blood glucose levels, as even small misinterpretations in these readings can significantly impact a diabetic patient’s health management strategy.
The origins of the formula for converting blood glucose measurements from mmol/L (millimoles per liter) to mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) lie in the fundamental principles of chemistry, specifically molar mass and concentration conversions.
Molar Mass of Glucose: The molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6. The molar mass (molecular weight) of glucose is calculated based on the atomic masses of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). One mole of glucose weighs approximately 180.16 grams (g/mol). This value is crucial in the conversion formula.
Concentration Units: mmol/L and mg/dL are two different ways to express the concentration of a substance in a solution. mmol/L is a molar concentration, indicating the number of moles of a substance per liter of solution. mg/dL, on the other hand, is a mass concentration, showing the mass of a substance in milligrams per deciliter of solution.
Conversion Formula: The conversion formula is derived from the relationship between molar mass and the concentration units. To convert mmol/L to mg/dL for glucose, you multiply the mmol/L value by the molar mass of glucose (180.16 g/mol) and then adjust for the unit difference between liters and deciliters.
Since 1 deciliter is one-tenth of a liter, and considering the mass in milligrams, the molar mass in g/mol needs to be adjusted accordingly. This results in the factor of approximately 18 (more precisely, 18.01559).
This conversion formula is essential in clinical settings, especially in the management of diabetes, where blood glucose levels need to be accurately measured and understood. Different regions of the world use different units (mmol/L is common in the UK, Canada, and Australia, while mg/dL is commonly used in the US), so this formula allows for consistent interpretation of blood glucose levels across different healthcare systems.
Check out this Easy-to-Use Calculator! RPM to Acceleration CalculatorUsing the Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator is straightforward. Follow these simple steps:
Navigating the world of blood sugar management is made easy with the user-friendly Mmol/L to mg/dL calculator. This essential tool is designed to help patients, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in health and wellness to effortlessly convert blood glucose measurements between two commonly used units: millimoles per liter (mmol/L) and milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Here’s a step-by-step guide to utilizing this simple yet powerful calculator:
Start with Your Measurement: Begin by entering your blood glucose level in the format of millimoles per liter (mmol/L) into the designated input field marked as “Mmol/L”. This unit is commonly used in countries like the UK, Canada, and Australia, and understanding it is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Instant Conversion with a Click: After inputting your mmol/L value, click on the “Calculate” button. This action triggers the calculator’s algorithm, which is designed based on the precise formula converting mmol/L to mg/dL, ensuring accuracy and reliability in every calculation.
View Your Results in mg/dL: The conversion result will promptly be displayed in the “mg/dl” output field. This value represents your blood sugar level in milligrams per deciliter, the preferred unit of measurement in the United States and many other countries. This instant conversion aids in a clearer understanding of blood sugar readings, facilitating better communication between international healthcare providers and patients.
Our Mmol/L to mg/dL calculator is a vital tool for anyone needing to convert blood sugar measurements quickly and accurately. This Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator is designed to streamline the process and provide clarity in blood sugar level readings across different measurement systems.
Let’s say you have a blood glucose level of 5.6 mmol/L. Here’s how you can use the calculator to convert it to mg/dl:
The result will show that 5.6 mmol/L is equivalent to 100.74 mg/dl.
Certainly! Here are a few real-life examples of how to use the Mmol/L to mg/dl calculator, each showcasing a different value conversion:
Example 1: Converting 7.8 mmol/L
Example 2: Converting 4.4 mmol/L
Example 3: Converting 9.2 mmol/L
Example 4: Converting 6.3 mmol/L
These examples provide practical scenarios that someone might encounter when monitoring blood glucose levels, whether for personal health management or in a clinical setting. By showing varied mmol/L values, these examples demonstrate the versatility and utility of the calculator across a range of blood sugar levels.
Understanding and accurately interpreting blood glucose levels is a critical aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health – The mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator helps with that. To aid in this process, especially in a global context where different measurement units are used, we present the ‘Reference Table for Converting Common Blood Glucose Levels from mmol/L to mg/dL’.
This Reference Table for Converting Common Blood Glucose Levels is an indispensable tool for patients, healthcare providers, and anyone involved in diabetes care or general health monitoring.
To help with Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator conversions, here’s a table showing several conversions from mmol/L to mg/dL using the formula:
| mmol/L | mg/dL |
|---|---|
| 4.0 | 72.06 |
| 5.0 | 90.08 |
| 5.6 | 100.89 |
| 6.5 | 117.10 |
| 7.0 | 126.11 |
| 7.8 | 140.52 |
| 8.5 | 153.13 |
| 9.2 | 165.74 |
| 10.0 | 180.16 |
The table above provides a quick reference for converting common blood glucose levels from mmol/L to mg/dL.
Blood glucose measurements are commonly reported in either millimoles per liter (mmol/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), depending on the geographical location. For instance, mmol/L is widely used in countries like the UK and Australia, while the United States and several other countries prefer mg/dL. This disparity can lead to confusion and misinterpretation of vital health data.
The Mmol/L to mg/dl calculator reference table above addresses this challenge by providing a straightforward conversion of common blood glucose values from mmol/L to mg/dL. By utilizing a precise and scientifically validated conversion factor, the table ensures accuracy and ease of understanding, bridging the gap between different measurement systems.
Check out this Easy-to-Use Calculator! Discomfort Index CalculatorBelow you can find an additional reference table with more real-life examples, showing the conversion of blood glucose levels from mmol/L to mg/dL:
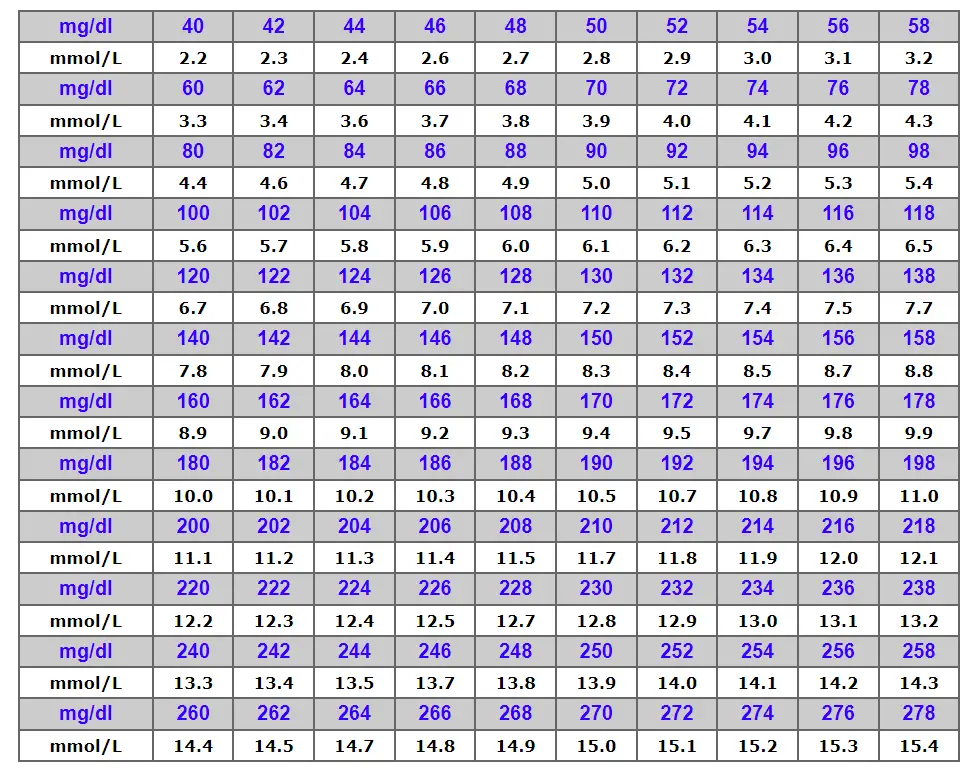
Here’s a simplified and more digestible version of the blood glucose levels table so you don’t need to use Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator:
| Category | mmol/L Range | mg/dL Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia | 1.7 – 3.3 | 30 – 60 |
| Normal Range | 4.0 – 5.5 | 70 – 100 |
| Hyperglycemia | 6.1 – 33.3 | 110 – 600 |
The difference between mmol/L (millimoles per liter) and mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) lies in the way they measure the concentration of substances, such as glucose in the blood. These two units are commonly used in the context of blood sugar levels, particularly in diabetes management.
Unit Composition:
Context of Use:
Application in Blood Sugar Measurement:
Conversion: The two units are convertible. The conversion factor is approximately 18.01559. This factor is derived from the molecular weight of glucose (180.1559 g/mol) and adjusts for the difference between moles and grams, and between liters and deciliters.
Understanding the difference and being able to convert between these two units is essential for accurate blood sugar management, especially for individuals with diabetes who may encounter both units in their care management. Different countries and medical practices use different units, so being conversant with both is important for the correct interpretation of blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar levels, or glucose levels in the blood, are crucial for several reasons, particularly in the context of overall health and the management of diabetes:
Energy Source for the Body: Glucose is a primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It is necessary for normal bodily functions, including brain activity, muscle work, and various metabolic processes.
Regulation of Metabolic Health: Proper regulation of blood sugar levels is essential for metabolic health. The body’s ability to maintain these levels within a normal range is vital for preventing both short-term and long-term health issues.
Diabetes Management: For individuals with diabetes, monitoring and managing blood sugar levels is essential. Diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to properly regulate blood sugar levels, which can lead to excessively high (hyperglycemia) or low (hypoglycemia) levels.
Check out this Easy-to-Use Calculator! Flat Bag Volume CalculatorPreventing Short-Term Complications:
Avoiding Long-Term Health Issues: Consistently high blood sugar levels over time can lead to long-term complications such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney damage (nephropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), and can affect many other organs and bodily systems.
Lifestyle Indicator: Blood sugar levels can also indicate the effects of lifestyle factors like diet, physical activity, and stress. Monitoring these levels helps in making informed decisions regarding diet, exercise, and stress management.
Guidance for Medication and Treatment: For people with diabetes, blood sugar levels help guide decisions regarding insulin dosing, the use of other diabetes medications, and dietary adjustments.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is fundamental for energy provision, metabolic health, prevention of diabetes-related complications, and overall well-being. Regular monitoring helps in managing diabetes effectively and in making lifestyle choices that contribute to long-term health.
Different regions and medical systems use different units of measurement for blood glucose levels. Converting between the two units ensures consistency and accurate interpretation of results.
Yes, the conversion factor remains constant for blood glucose conversions from mmol/L to mg/dl.
The reference range for normal fasting blood glucose levels is approximately 70-100 mg/dl (3.9-5.6 mmol/L).
No, this calculator specifically converts between mmol/L and mg/dl for blood glucose levels.
The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on your health condition. Consult with a healthcare professional for specific guidance.
“Mmol/L” stands for millimoles per liter, and “mg/dl” stands for milligrams per deciliter.
Incorrect conversions could lead to misinterpretation of blood glucose levels, which may affect medical decisions. It’s important to use the correct units.
It’s advisable to keep the result accurate by not rounding it until needed for reporting.
Consult healthcare professionals or medical resources for in-depth information about blood glucose measurement.
The Mmol/L to mg/dl Calculator simplifies the process of converting blood glucose levels between different units of measurement. This tool ensures that individuals can accurately interpret their results, regardless of the regional or system-specific units used. Keeping blood glucose levels in check is crucial for managing various health conditions, and this calculator serves as a valuable resource for this purpose.
In our detailed discussion, we explored the intricacies of the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, a crucial tool in the realm of diabetes management and general health monitoring. This calculator facilitates the conversion of blood glucose levels from mmol/L (millimoles per liter) to mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter), a process pivotal for those monitoring diabetes across different regions with varying measurement units. We delved into the formula used by the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, which involves multiplying the mmol/L value by approximately 18.01559. This factor, derived from the molecular weight of glucose, enables the transition from a molar concentration to a mass concentration, making it a key component in understanding and managing blood glucose levels.
Enhancing this exploration, we provided practical examples and constructed comprehensive reference tables. These resources not only demonstrated specific conversions using the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator but also categorized blood glucose levels into essential ranges such as hypoglycemia, normal range, and hyperglycemia. Such categorization is vital for individuals and healthcare professionals to accurately interpret blood sugar readings and make informed decisions regarding health and diabetes management.
The significance of maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, a primary focus of the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, is paramount in both medical and personal health contexts. These levels are critical for energy provision, metabolic health, and the effective management of diabetes. Proper regulation of blood sugar, as indicated by the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, helps in preventing immediate health risks and long-term complications associated with diabetes. Regular monitoring and understanding these levels, facilitated by tools like the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, are essential for lifestyle management and treatment planning, especially for diabetic patients.
To aid in the visual comprehension of this topic, we created an abstract, minimalistic illustration suitable as a WordPress Featured image. This image, designed to complement the use of the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, employed color gradients to symbolize different blood glucose ranges, thereby providing an intuitive visual guide to understanding these measurements.
Throughout this discussion, our focus was on presenting the complex medical information associated with the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator in an accessible and clear manner. By offering real-world applications, simplified tables, and visual aids, we strived to make the usage and understanding of the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator more approachable for a diverse audience. Whether it’s for personal health monitoring, professional medical use, or general education, the insights and tools provided, including the Mmol/L to mg/dL Calculator, offer invaluable assistance in the critical area of blood sugar level management.